© 2009 Er. Jagvir Goyal
Note: This highly informative and elaborate paper was written by the Author many years back and holds valuable information. Readers should update themselves with the latest developments that might have occurred after the presentation of this paper.
The necessity: The first word that comes to mind whenever we talk of infrastructure development is ‘Concrete’. Images of flyovers, bridges, skyscrapers, chimneys, cooling towers fill our mind and it dawns upon us that today, anything is possible with concrete and almost nothing without it. Clearly, infrastructure development has multiplied the demands for concrete many times. Also coupled with this demand for quantity is the quality of concrete. Quantity can’t be increased at the cost of quality and for proper quality of concrete, its production, transportation, placement and compaction need to be done in a perfect manner. Two main criteria determining the quality of concrete are its strength and durability. And achievement of Strength and durability of concrete begins with its proper production. Concrete if produced properly means a battle half won. The ease with which the quality control measures can be taken at the production stage itself is not available at later stages of transportation and placement of concrete. Quality control at production level can be well achieved by using a batching plant. Installing a batching plant at site has therefore become a basic necessity for all the infrastructure projects being handled today.
RMC Vs Batching plant: A Ready Mix Concrete plant is installed at a location with an aim to carry the business of selling concrete while a Concrete Batching Plant is installed at the site itself for in-situ production of concrete. A RMC plant also has a batching plant at its back. Both aim at producing concrete under fully controlled conditions. Big power projects including thermal, nuclear or electric-hydro ones and transportation projects like bridges, flyovers and cloverleaves can’t come up unless a batching plant is installed at site. Concrete batching plants, once singular or uncommon are becoming an essential equipment now.
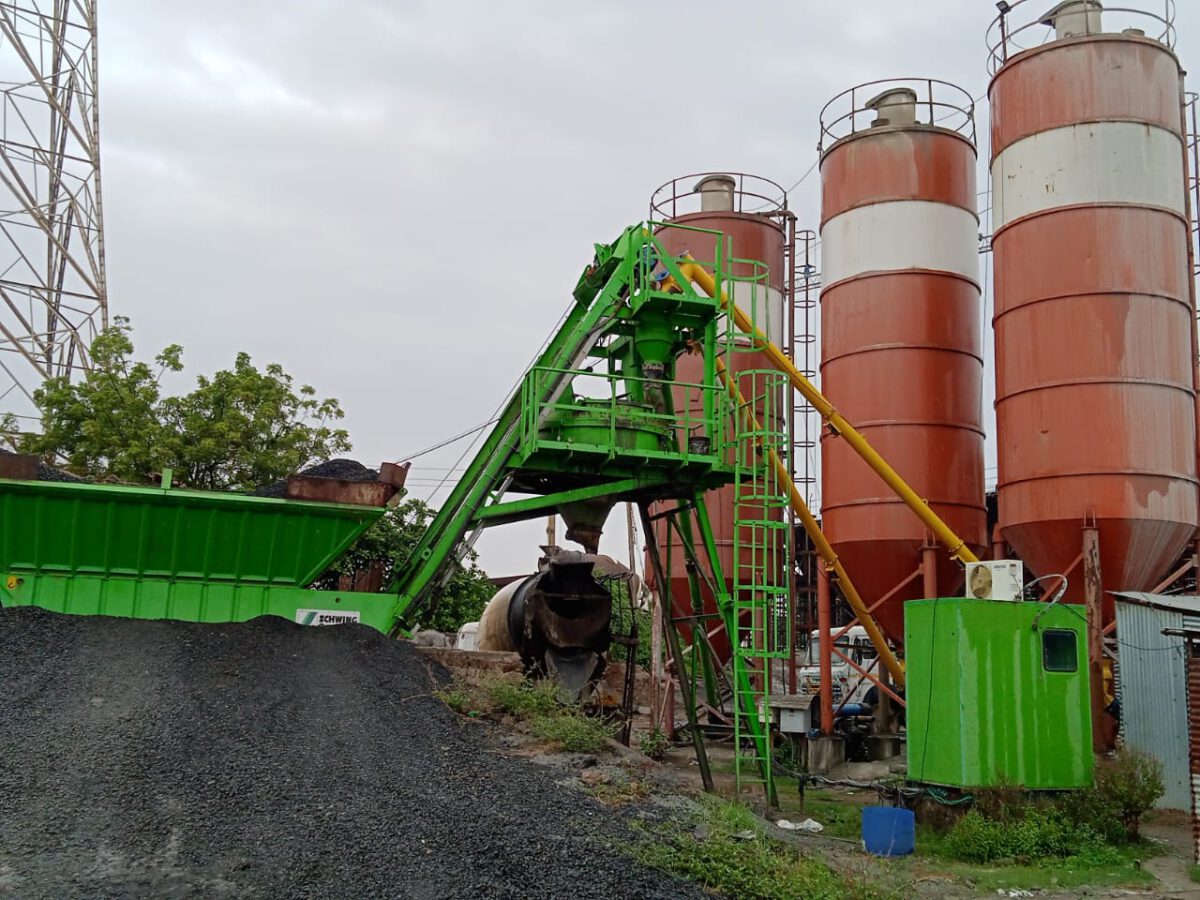
Batching plants: Concrete Batching plants with varying capacities of 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 240 and 330 cubic metres per hour are now being produced in India by using fully imported mixing units. Lower capacity pumps are more in demand. Depending upon the daily requirement of concrete at site, suitable capacity of the plant can be chosen.
Components of a batching plant: A concrete batching plant has the following essential components-
- Storage equipment.
- Batching equipment.
- Mixing equipment.
- Control systems.
- Enabling equipment.
- Access equipment.
- Conveyor system.
The capacity or output of each of these components is linked to the capacity of the batching plant.
Storage equipment: The storage equipment consists of Cement Storage silos, Aggregate storage bins, Admixture storage tanks and water storage tanks. Both bagged as well as container filled cement can be loaded in these silos through suitable pneumatic systems. The aggregates can be stored in silos positioned above the mixing unit or in bins near the mixing plant. In case of storage in bins near the mixing plant, a dragline is required to feed the required quantity of aggregates to the mixing plant. Star type batching plants therefore need additional equipment for feeding of aggregates to the mixing plant.
Batching equipment: Batching equipment provides all ingredients by weight. Volumetric equivalents are not used as some error may crop up in that. Batching by weight is best and most accurate. Therefore, load cells are used and weigh batching of cement, aggregates and admixtures is done. Even water is added by weight by use of pulse meter or water gauge. Cement hopper is self cleansing type and is connected to the mixing unit through a hose to avoid any pollution. The type of aggregates to be used need to be pre-decided as their number affects the batching plant specifications. Normally, a batching plant may allow use of maximum 4 types of aggregates. Maximum size of aggregate is also required to be fixed. 40 down aggregate is allowed if percentage retention on 40 mm sieve is discarded. When there are frequent changes in plant locations, compartment type batcher is preferred. Aggregate loading is done by a front end loader to a conveyor belt or a ramp built for the purpose. While fine aggregate needs a vibrator to ensure its free flow to the loader, scrapers are required in bins to scrape the aggregates towards the flap gates.
Mixing equipment: The mixers used for mixing of concrete ingredients play a pivotal role in deciding the quality of concrete produced. For small capacity batching plants, pan type or drum type mixers are used while for large capacity plants, twin shaft mixers are most suitable. Twin shaft mixers ensure better mixing of concrete and save time. There are Turbo mixers that carry spring mounted mixing arms protected by wear resistant polyurethane (PU) covering. The blades are adjustable. The inner cylinder is lined with 8 to 10 mm thick anti-wear and tear plates. In the mixing plant, hydraulically actuated discharge flaps with a limit switch for open and closed positions and run by a hydraulic pump deliver compacted concrete having two-third quantity of the volume of dry ingredients. Additional hydraulic pump for emergency discharge of concrete is another feature of the mixing plant. Better equipped mixers have a mixer trough covering, hinged cover in mixer trough covering, safety switch for automatic stoppage of mixer on opening of hinged cover and a sight flap. Concrete mixing time in twin shaft mixers is just 25 to 30 seconds per batch instead of normal mixing time of 2 minutes. Thus there is a lot of time saving with twin shaft mixers.
Control systems: Use of fully automatic micro computer control system ensures complete control over concrete production. It can give directions for adding 4 types of aggregates, cement, water and admixtures as per one of about 100 mix designs normally stored in its memory. The number of mix designs can be as high as 10000. Control systems allow switching over to manual system also. Emergency cut-off is also available for use if erroneous entries have been made. Digital displays for all weighing systems for cement, water, admixture and aggregates are part of the control system. Number of batches released and pending production can be viewed on the control panel. Batch log print outs can also be issued by it. The control panel also has the facility of moisture correction for sand and water. Measurement of moisture in sand and accordingly, automatic reduction in quantity of water can be done.
Enabling equipment: It includes power supply equipment, compressed air equipment and hoses, cabling, electromagnetic pneumatic valves for actuation of batching gates, pneumatic system for discharge gates and other miscellaneous equipment for smooth coordination and functioning of all components. The compressor should be equipped with compressed air tank of sufficient capacity, three phase drive motor, pressure gauges, pressure adjusting devices. Its suction volume and maximum pressure parameters should be examined.
Access equipment: The batching plant should have easy access provisions for each component. An operator’s stand should be available. Access ladders to the operator’s platform and mixer platform are provided.
Conveyor system: Batching plant is equipped with mixer discharge hopper with rubber hose to fill the transit mixers, feeder skip, screw conveyor of suitable diameter for cement with length generally varying from 10 to 12 metres.
Dimensions: A batching plant producing 30 cubic metres of concrete per hour should have a weight of 8 tonne and a 40 feet trailor truck should be able to transport it from the works to site. Its height shall be about 8 metres and length and breadth about 2.5 metres each. Power load shall be about 50 KW. However dimensions vary for different plants produced by different manufacturers.
Preparation for installation of batching plant: Whenever orders are placed upon a firm for supply and installation of a batching plant, certain issues over site facilities should be sorted out at the time of placing the order so that no problems arise during installation period. The following issues should be looked into:
- Foundations-Their size and details are to be provided by the supplier. The scope of their provision needs to be defined.
- Scope of provision of cranes for assembly of equipment at site needs to be defined. Sometimes, the cranes are available with the purchaser and he can provide the same to the supplier for use and can negotiate on this account.
- Plumbing and water supply provisions. (Installation of a pump may be necessary).
- Electric supply connection and cabling network for various equipments at desired ratings.
- Air conditioning services.
- Earthing arrangements for equipment.
- Calibration arrangement of gauges.
Generally, an equipment supplier will not include these items in his scope and will demand their provision at site. The client should therefore ensure their provision or negotiate with the equipment supplier for these arrangements at his level.
Selection of the batching plant: Once the capacity of the batching plant required at site is determined by keeping in view the concrete requirements, a survey of the various brands available can be done. Ideally, an imported plant should be chosen if the desired concrete output is large while an indigenously produced plant can be chosen for smaller capacities. Past performance of the equipment manufacturers should always be studied before making final decision. Only a satisfactory performance in the long run wins the confidence of civil engineers for future recommendations. The following factors should be studied while selecting a batching plant:
- Minimum wear and tear: The components of the batching plant should undergo minimum wear and tear despite its constant use. The warranty period and clauses should be carefully considered.
- Minimum energy consumption: It is another important factor to look into to minimize running expenses of the batching plant.
- Minimum maintenance requirements: The batching plant should be able to withstand rough handling and demand minimum maintenance.
- Multiple mix design options: It must have multiple mix design options available. A batching plant needs to be shifted from site to site on completion of projects and different mix designs are required to be followed at different sites as per strength and workability requirements of concrete and the quality of locally available aggregates.
- Accurate weigh batching of concrete ingredients: The batching plant must have accurate weigh batching systems in it, with electronic controls and calibrated gauges for measurements.
- Emergency stoppage arrangements: The plant should be equipped with automatic emergency stoppage arrangements in case of emergencies to avoid any sort of accidents at site.
- Low consumption of consumables: In addition to low power consumption, the plant should have low consumption of consumables such as oils too to minimize running expenses.
- Automatic controls: Most of the activities in the running of the batching plant should be under automatic controls. Once the directions are fed, the plant should be able to read and operate automatically. However manual switchover options should be available.
- Easy availability of spares: Sales are today combined with service and spare activities in most of the companies. However, it should be ensured that spares are easily available for replacements as and when required. In addition service and repairs should be prompt. Companies track record can be considered for this.
- Safe running of plant: Safety features of the plant should be studied. Easy to access, easy to escape, safety against dust and smoke, proper insulation against any shocks should be some essential features.
- Noise pollution: The plant should make minimum noise during its operation. Sooner or later, noise pollution regulations are likely to be imposed in India too.
Old Vs New: It is better to buy a new batching plant rather than buying an old one at a lower cost. If the economics of the project doesn’t permit buying a new plant, the option of hiring a batching plant on rental basis should also be considered. An old batching plant may always present unpredictable problems and its repair & replacement expenses may be high.
Cost considerations: Big players and suppliers like Schwing Stetter have arrived in India and supplying batching plants at quite competitive prices. Last few years have seen an incredible improvement in Batching plant equipment. These are now being made fully automatic and trouble free. Schwing has installed about 500 batching plants in India with concrete production capacity of 30 cum per hour or lesser. Not only this, this firm has set up spare part outlets in Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bangalore and Ahmedabad. A 30 cum per hour capacity plant should cost around Rs. 35 lacs plus taxes in India. Many Indian firms are offering batching plants at quite competitive rates with post-installation service and warranty. Universal construction machinery has supplied more than 200 batching plants of small and medium size in the country.
While placing an order: Whenever an order for supply of a batching plant is placed by a builder or contractor upon an equipment manufacturer, besides the site facilities explained above, certain issues should be further sorted out. These include the time to be taken by the supplier. Generally, a supplier may need 6 to 7 weeks to meet a customized order. Next, the issue of erection of equipment at site, its commissioning and trial run should clearly be included in the scope of supplier. Not only this, he should provide training to certain operation and maintenance personnel of the buyer. This will in fact go in favor of supplier also as trouble free running of the plant will add to his credit. Non availability of trained operators is becoming a major problem at Indian projects. Mishandling of equipment by untrained operators sometimes costs very heavily to the builder or construction company. The issue of transportation of equipment from the works to site or bearing its cost should be sorted out. Transit insurance, providing a tool kit to the buyer, cost of consumables and unskilled labor required during installation are other issues to look into for smooth execution of the deal.
Foundations for batching plants: A very important issue to be looked into is the size of the foundations required for the installation of batching plant. Laying heavy foundations at a site and later, their removal on completion of a project and restoration of the ground to original conditions is a major irritant for the construction companies. Batching plants requiring least foundations can present it as an attractive feature of their equipment. Equipment giants like Stetter have devised mobile batching plants with compartment batchers that can be set up directly on the ground and need no foundations. Compartment batchers may have net storage capacity up to 70 cubic metres. Even cement silos of capacity up to 95 cubic metres are on mobile foundations. Trough mixers or twin shaft mixers are used in mobile plants. Twin shaft mixers ensure production of quality concrete with short mixing times. Fully automatic pump and nozzle system adds weighed quantity of water to the mixer. Mobile batching plants with concrete output of about 100 cubic metres per hour are now available in India. Size of these mobile plants is as large as 5000 sq.ft. to 7000 sq.ft. Non-requirement of foundations is likely to make them more popular.
Optimum performance of batching plants: Manufacturers should provide suitable guidelines to the users to generate best and trouble free output of the batching plants. In addition to defining batch size and maximum size of aggregate some operational tips should be listed and pasted within operator’s eye view. Time intervals for replacements of lubricants and oils and correct air pressures should also be exhibited.